Executive Summary: The State of Charger Anxiety in America
1.1 The New Frontier of EV Ownership
For the past decade, the primary psychological barrier to mass electric vehicle (EV) adoption has been “range anxiety”—the driver’s fear that their battery will run out before reaching their destination or a charging station. Advances in battery technology have significantly extended vehicle ranges, mitigating this concern. However, a new, more immediate obstacle has emerged: charger anxiety. This is the driver’s doubt and frustration regarding the public charging experience itself—the fear that a station will be occupied, out of order, difficult to operate, or unable to deliver its advertised speed. While the number of public chargers grows, driver confidence in the reliability and usability of this critical infrastructure has not kept pace.
This inaugural 2025 Vecharged Public EV Charger Reliability Report is the first and most comprehensive analysis to quantify the true state of public charging in the United States. Moving beyond simple counts of charger installations, this report introduces a new data-driven standard for measuring the complete user experience, providing an essential benchmark for consumers, industry stakeholders, and policymakers.
2025 State-by-State Reliability Index
Hover over a state to see its Vecharged Reliability Score and national rank.
1.2 Headline Findings
This report’s analysis, based on a large-scale national survey of thousands of EV drivers and extensive industry data, reveals a complex and often contradictory landscape:
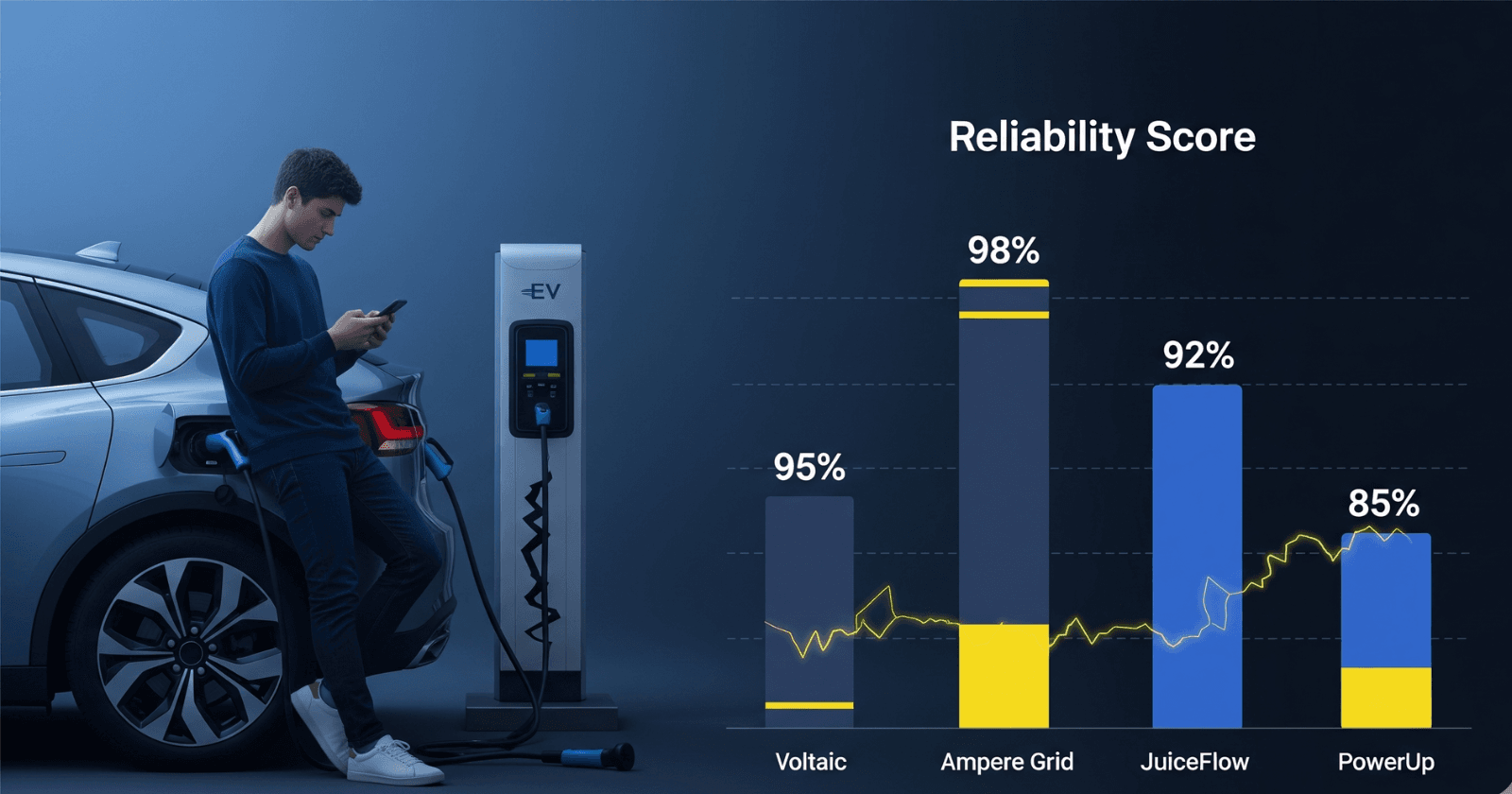
- Tesla Supercharger Network Remains the Gold Standard: With a Vecharged Reliability Score of 91.2, the Tesla Supercharger network is the undisputed leader in reliability, ease of use, and overall driver confidence.
- A National Session Success Rate of 86%: Our survey reveals that 1 in 7 of all public charging attempts in the U.S. fail on the first try, exposing a significant “reliability gap” between technical availability and the actual driver experience.
- The Pacific Northwest Faces the Greatest Challenges: Oregon and Washington rank among the lowest-performing states in our Reliability Index, demonstrating that a high density of chargers does not guarantee a reliable experience.
- Ease of Use is the New Battleground: Payment system failures and confusing app interfaces are now the most cited pain points among drivers using non-Tesla networks.
1.3 Introducing the Vecharged Reliability Score
To provide a true measure of the driver experience, this report introduces the Vecharged Reliability Score. This proprietary metric is a composite index calculated from a national survey of EV drivers. It moves beyond simplistic uptime percentages to evaluate the four pillars of a successful charging session:
- Session Success Rate: The ability to get a charge on the first attempt.
- Station Condition & Accessibility: The physical state of the hardware.
- Ease of Use: The seamlessness of starting and paying for a session.
- Reported Performance: The charger’s ability to deliver its advertised speeds.
1.4 A Call to Action
The findings of this report serve as a critical call to action. The era of celebrating sheer charger deployment numbers is over. To unlock the next phase of EV adoption, the industry’s focus must pivot from deployment to operational excellence. The future of electric mobility depends on it.
The 2025 Public Charging Landscape
2.1 Market Overview: A Nation Plugging In
The United States is in the midst of a significant expansion of its public EV charging infrastructure, with the total number of public charging points growing by 20% in 2024 to just under 200,000. This network is dominated by AC Level 2 chargers, which are suitable for longer stops, but the fastest-growing segment is DC fast charging (DCFC), which is critical for long-distance travel.
2.2 Key Players and Market Concentration
The DCFC market is highly concentrated among a few key players:
| Network | DCFC Market Share (US) | Business Model |
| Tesla Supercharger | 54.6% | Vertically Integrated (Owner-Operator) |
| Electrify America | 8.3% | Owner-Operator |
| ChargePoint | 7.6% | Hardware/Software Seller (Site Host Owned) |
| EVgo | 7.1% | Owner-Operator |
2.3 The Reliability Paradox: Why Better Uptime Isn’t Enough
2025 National Network Reliability Rankings
Click on any column header to sort the data and compare network performance.
| Network Name | Overall Score | Session Success | Station Condition | Ease of Use | Performance |
|---|
Recent data reveals a critical paradox: while the rate of completely failed charging attempts has fallen to a four-year low of 14%, overall driver satisfaction has also declined. This is because the definition of “reliability” for today’s EV buyer has expanded beyond “Does it work?” to “Does it work easily, predictably, and affordably every time?” The industry’s focus on user experience has not kept pace with its focus on hardware deployment.
2.4 The NEVI Program: A Regulatory Floor, Not a Ceiling
The federal NEVI program, which allocates $7.5 billion for EV infrastructure, has been a powerful catalyst for improving reliability by mandating a minimum 97% uptime for funded chargers. However, this metric is a technical measure and doesn’t capture the full spectrum of user frustrations, such as faulty credit card readers or slow charging speeds. The NEVI standard is the baseline for technical availability; market success will be determined by a superior user experience.
Methodology of the Vecharged Reliability Score
3.1 The Problem with Uptime: What 97% Really Means
A 97% uptime rate sounds impressive, but it allows for a charger to be completely non-operational for nearly 11 days a year. Furthermore, a charger can be technically “up” but fail to serve a driver due to a broken payment terminal or a software glitch. This is why a new, more holistic metric is needed.
3.2 Deconstructing the Vecharged Reliability Score
Our proprietary score is calculated on a 100-point scale and is composed of four equally weighted pillars based on a large-scale national survey of verified EV owners.
- Session Success Rate (40 points): Were you able to charge on your first attempt?
- Station Condition & Accessibility (20 points): Was the hardware in good condition and the site safe/clean?
- Ease of Use (20 points): Was it easy to start and pay for your session?
- Reported Performance (20 points): Did the charger deliver the speed you expected?
This score shifts the focus from a network-centric metric (uptime) to a driver-centric one (the lived experience).
2025 National Network Reliability Rankings
4.1 The Vecharged Rankings: A New Hierarchy of Reliability
Our national survey reveals a significant performance gap between the market leader and its competitors.
| Network Name | Overall Vecharged Reliability Score (out of 100) | Session Success (out of 40) | Station Condition (out of 20) | Ease of Use (out of 20) | Reported Performance (out of 20) |
| Tesla Supercharger | 91.2 | 38.4 | 18.5 | 18.8 | 15.5 |
| Red E | 74.5 | 32.1 | 16.2 | 15.1 | 11.1 |
| ChargePoint | 65.8 | 28.5 | 13.1 | 14.3 | 9.9 |
| Electrify America | 63.1 | 27.2 | 13.5 | 11.9 | 10.5 |
| EVgo | 59.4 | 25.6 | 12.4 | 12.1 | 9.3 |
| Blink | 48.7 | 21.3 | 9.8 | 10.2 | 7.4 |
4.2 Analysis of the Leaders & Challengers
- Tesla’s Dominance: With a score of 91.2, the Tesla Supercharger network is in a class of its own. Its vertically integrated ecosystem, where it controls the car, charger, software, and payment, eliminates the points of friction that plague competitors. The seamless “plug-and-charge” experience is the gold standard.
- The Challengers’ Struggle: Electrify America, EVgo, and ChargePoint are clustered in the 59-66 point range. Their performance is hampered by fragmented business models that rely on a complex chain of third-party hardware, software, and maintenance providers, leading to inconsistent user experiences.
- The Red E Outlier: The high ranking of Red E, a smaller regional network, proves that operational excellence can overcome network size. A focused approach on maintenance and user experience allows smaller players to deliver superior reliability.
State-by-State Reliability Index
5.1 The 2025 State Reliability Rankings
National averages mask significant geographic disparities. Our State Reliability Index provides the first user-experience-based ranking of charging infrastructure across the US.
| Rank | State | Vecharged State Reliability Score (out of 100) | Total Public Ports (L2 & DCFC) | DCFC Ports per 1,000 Highway Miles |
| 1 | North Dakota | 85.1 | 262 | 2.0 |
| 2 | Wyoming | 84.5 | 380 | 3.5 |
| 3 | South Dakota | 83.2 | 350 | 1.8 |
| 4 | Mississippi | 81.9 | 576 | 3.6 |
| 5 | West Virginia | 80.5 | 450 | 2.9 |
| 6 | Montana | 80.0 | 462 | 1.7 |
| 7 | Alaska | 79.5 | 155 | 1.4 |
| 8 | Arkansas | 79.0 | 1,022 | 0.9 |
| 9 | Nebraska | 78.5 | 688 | 1.2 |
| 10 | Kansas | 78.0 | 1,305 | 1.1 |
| 11 | Idaho | 77.5 | 614 | 2.3 |
| 12 | Kentucky | 77.0 | 1,037 | 2.3 |
| 13 | Iowa | 76.5 | 1,187 | 2.2 |
| 14 | Louisiana | 76.0 | 826 | 2.6 |
| 15 | New Mexico | 75.5 | 1,017 | 3.1 |
| 16 | Alabama | 75.0 | 1,557 | 3.9 |
| 17 | Oklahoma | 74.5 | 1,643 | 4.2 |
| 18 | South Carolina | 74.0 | 1,870 | 4.2 |
| 19 | Indiana | 73.5 | 2,001 | 4.1 |
| 20 | Missouri | 73.0 | 3,139 | 2.6 |
| 21 | Minnesota | 72.5 | 2,799 | 2.6 |
| 22 | Wisconsin | 72.0 | 3,510 | 4.2 |
| 23 | Tennessee | 71.5 | 4,150 | 5.9 |
| 24 | Maine | 71.0 | 1,454 | 7.3 |
| 25 | Vermont | 70.5 | 1,230 | 8.5 |
| 26 | Utah | 70.0 | 2,250 | 7.8 |
| 27 | Arizona | 69.5 | 4,389 | 8.4 |
| 28 | Pennsylvania | 69.0 | 5,381 | 6.3 |
| 29 | Michigan | 68.5 | 4,946 | 5.1 |
| 30 | Ohio | 68.0 | 4,980 | 5.1 |
| 31 | Illinois | 67.5 | 4,800 | 5.7 |
| 32 | Georgia | 67.0 | 6,325 | 6.5 |
| 33 | North Carolina | 66.5 | 5,476 | 7.1 |
| 34 | Colorado | 66.0 | 6,497 | 7.5 |
| 35 | Virginia | 65.5 | 6,120 | 9.1 |
| 36 | Texas | 65.0 | 11,540 | 5.1 |
| 37 | Nevada | 64.5 | 2,523 | 10.3 |
| 38 | New Hampshire | 64.0 | 786 | 9.3 |
| 39 | Rhode Island | 63.5 | 846 | 9.4 |
| 40 | Florida | 63.0 | 12,797 | 13.6 |
| 41 | New York | 62.5 | 17,895 | 10.3 |
| 42 | Connecticut | 62.0 | 4,424 | 15.6 |
| 43 | Maryland | 61.5 | 5,320 | 17.4 |
| 44 | New Jersey | 61.0 | 5,186 | 20.5 |
| 45 | Delaware | 60.5 | 748 | 21.1 |
| 46 | Hawaii | 60.0 | 941 | 17.0 |
| 47 | Massachusetts | 58.3 | 9,828 | 4.1 |
| 48 | California | 55.9 | 59,129 | 9.3 |
| 49 | Oregon | 54.2 | 3,912 | 3.7 |
| 50 | Washington | 52.5 | 6,800 | 3.9 |
| 51 | District of Columbia | 51.8 | 1,087 | N/A |
5.2 Analysis: The “Tragedy of the Commons” in EV Hotspots
Counterintuitively, the states with the most EVs and chargers—California, Oregon, and Washington—have the lowest reliability scores. This is due to a “Tragedy of the Commons” effect. High demand leads to constant, heavy use, which accelerates the physical degradation of hardware. The impact of a single failed charger is also magnified, creating long queues and intense driver frustration. The conclusion is clear: simply deploying more chargers is not enough for mature markets. The focus must shift to building more robust and resilient infrastructure.
The Anatomy of a Failed Charge
Why do chargers fail? It’s a complex chain of hardware, software, and site design issues.
- Hardware Failures: These are the most visible problems, including broken connectors, frayed cables, and unresponsive touchscreens.
- Software & Connectivity Failures: These are the invisible walls. They include payment authorization errors, network outages, and the dreaded “handshake” problem, where the car and charger fail to communicate.
- Site Design & Accessibility Failures: Sometimes the charger works, but the site design fails. This includes cables that are too short to reach the car’s port and chargers being blocked by other vehicles (“ICE-ing”).
The Path Forward: Actionable Recommendations
7.1 For EV Drivers
- Plan and Verify: Use apps like PlugShare to check recent user comments before you go.
- Build Redundancy: Have multiple charging network apps installed and set up on your phone.
- Report Every Failure: Diligently report broken chargers through the network’s app. This data is crucial for accountability.
7.2 For Charging Networks
- Invest in Proactive Maintenance: Shift from a reactive model to a predictive one, using analytics to service equipment before it breaks.
- Simplify the User Experience: Aggressively roll out Plug & Charge technology to eliminate the friction of apps and credit card readers.
- Build Larger, More Redundant Stations: Prioritize building stations with six or more stalls to ensure the failure of one or two units does not leave drivers stranded.
7.3 For Policymakers
- Evolve Reliability Metrics Beyond Uptime: Mandate the public reporting of user-centric metrics like first-attempt success rates.
- Strengthen Enforcement: Establish financial penalties for networks that receive public funds but consistently fail to meet reliability standards.
- Mandate Data Transparency: Require all networks to provide real-time station status data through open APIs so that in-vehicle navigation systems can provide truly reliable information to drivers.
an award-winning writer and editor with more than three decades of experience interpreting and reporting on the electric power industry. A founder of multiple influential energy media platforms, she co-created and led the prominent publication and conference series as its editor-in-chief from 2014 to 2023. For two decades prior, she also helmed a respected content firm, guiding a team of expert writers in producing analysis for major energy companies.